Scabies
Condition Basics
What is scabies?
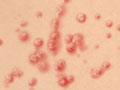
Scabies is a condition of very itchy skin caused by tiny mites that burrow into your skin. The itching is caused by an allergic reaction to the mites.
Scabies spreads very easily from person to person. It can affect anyone. It spreads more easily in crowded living situations or between close contacts.
With treatment, the scabies mites die and the itching goes away over a period of days to weeks. Without treatment, the mites continue to reproduce under the skin, causing more bumps and itching.
How does it spread?
Scabies mites spread from person to person by close contact. They can easily spread between people who live together, sleep in the same bed, or have sex. Sometimes the mites can also be spread by sharing towels, clothing, and other personal items.
Scabies often affects several household members at the same time. You can spread it to another person before you have symptoms.
What are the symptoms?
Scabies has two main symptoms:
- Severe itching that is usually worse at night.
- Tiny bumps, blisters or sores. Children tend to have worse skin reactions than adults.
Symptoms are more likely to occur:
- Between the fingers and on the palm side of the wrists.
- On the back of the elbows and in the armpits.
- Around the waistline and navel.
- On the buttocks.
- Around the nipples, the bra line, and the sides of the breasts.
- On the scrotum and penis.
In babies and small children, itching and skin irritation may also occur on the scalp, neck, and face and on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
If you have many scaly, crusted sores, you may have a rare form of scabies called crusted scabies.
How is it diagnosed?
Usually a doctor can diagnose scabies based on your symptoms. Scabies is especially likely if you have had close contact with other people who have had the same symptoms. Sometimes you may have a test to confirm that you have scabies.
How is scabies treated?
Scabies won't go away on its own. To get rid of it, and to keep from spreading it to others, you need to use medicine. You might use a special cream that your doctor prescribes. Or your doctor may have you take pills.
Be sure to read and follow all instructions that come with your medicine. A second treatment may be needed 1 to 2 weeks after the first treatment. Most creams or lotions are applied to the entire body. With infants and young children, apply the cream or lotion to the head and neck too.
Children can usually return to day care or school the day after the first treatment is completed.
Some scabies medicines aren't safe for infants younger than 2 months, children, older adults, and people who are pregnant or breastfeeding. To avoid dangerous side effects, be sure to follow your doctor's instructions carefully.
If you have scabies, you and anyone you have close contact with must all be treated at the same time. This keeps the mites from being passed back and forth from person to person.
After treatment, the itching usually lasts another 2 to 4 weeks. If you still have symptoms after 4 weeks, you may need another treatment.
Credits
Current as of: November 16, 2023
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: November 16, 2023
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.